Correlation of Spin Parameters with the Masses and Ages of some Barred Spiral Galaxies
Keywords:
Galaxies, Barred Spiral galaxies, Spin parameterAbstract
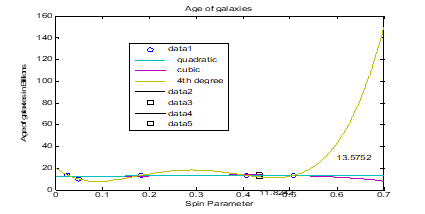
Cosmology is the study of the universe, or cosmos, regarded as a whole. Stars are collected into galaxies, galaxies are gravitationally bound into clusters, and even clusters of galaxies are found within larger superclusters. Galaxies are classified depending on their morphology: elliptic, lenticular, spiral or irregular. It is particularly interesting to study the structure of spiral galaxies, which is usually well differentiated in a central bulge, with a high concentration of stars, and a flat disk made up with younger stars, dust and gas. The arm of this work is to determine correlation between spin parameters, the total masses, gas masses and ages of some barred galaxies. The spin parameter happen to be the cardinal tangible parameter in verifying the morphological and visual feature of a spiral galaxy. Starting from the theoretical spin parameter equation suggested by Peebles, we analyzed the spin parameters of some barred galaxies using . In determining the correlation we use the Bravais Pearson correlation and made predictions using polynomial in MATlab.The spin parameter for Milky Way galaxy is 0.0253 which is in agreement with what is recorded in many literatures, Andromeda is 0.0491. The predicted ages for NGC 4258 was 12.63 billion years. In this work spin parameters of ten barred galaxies were calculated and their correlations gotten.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
How to Cite
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Osarodion Ebomwonyi, Emmanuel A. Oguche, Emmanuel O. Aiyohuyin, Determination of the η Parameter as function of Neutrino Mass: A Theoretical Approach , Nigerian Journal of Physics: Vol. 32 No. 4 (2023): Nigerian Journal of Physics - Vol. 32 No. 4




