In-Situ Gamma-Ray Logging as Diagnostic Tool for Failed Cased Water-Supply Boreholes, Lagos State
Keywords:
Aquifer, Borehole failure, Gamma-ray, ScreenAbstract
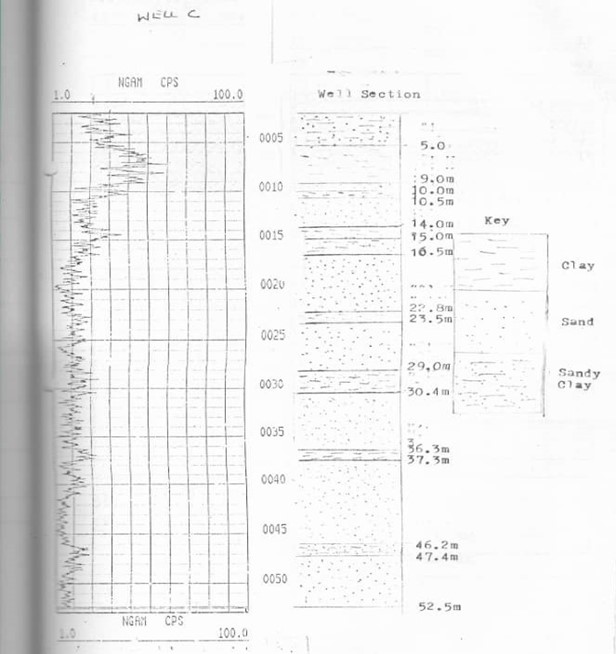
Frequent failure of water-supply boreholes in Lagos State, Nigeria, is often linked to poor delineation of sand-clay sequence within Coastal Plain Sands and recent alluvium. This study applies in-situ gamma-ray (GR) logging to diagnose the causes of failure in existing boreholes and to guide targeted rehabilitation. Continuous gamma-ray logs were acquired in a set of two non-productive or short-lived boreholes in Isolo, Lagos State. Log motifs were interpreted to distinguish clean, water-bearing sands (low GR) from clay-rich or silt horizons (high GR). Gamma-ray derived lithology picks were integrated with caliper logs of same boreholes. Results show that the failures are attributable to screen placement within or straddling high gamma-ray clay/silt intervals; targeting of thin sand bed bounded by clay layers that rapidly foul screens; incomplete casing through upper clay layer that allow fine particles migration and casing corrosion. The study demonstrates that in-situ gamma-ray logging is a rapid, low-cost tool for post-failure evaluation, enabling evidence-based decisions on borehole rehabilitation, optimal screen setting, and future well siting in Logos’ heterogeneous coastal aquifer system. This study also confirms beyond doubt the usefulness of gamma-ray logs for accurate borehole design and the importance of borehole geophysics for subsequent continual monitoring of groundwater quality of producing boreholes.